This could be rephrased to be - What are the parameters of a projection welding process? In this case what parameters should be checked besides pressure, current and time when projection welding (PCT)? Before we move on, these three cannot be passed over. If the control or force application is not functioning properly the projection weld will not meet specification. The appropriate components must be part of the regular preventive maintenance list and checked daily, weekly, monthly as prescribed. A guide to machine and equipment maintenance can be found in:
AWS J1.2 GUIDE TO INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE OF RESISTANCE WELDIGN MACHINES
The next areas to address are the conditions of:
FORCE APPLICATION AND FOLLOW-UP
This machine function insures that the projections have the proper force applied quickly and as the projection collapses the force is able to be maintained during the collapse. If the force function fails or hesitates at this critical time the strength of the weld can be compromised.
ALIGNMENT
Proper alignment of the machine/gun/tooling is critical to insure that the projections are all forced against the target part equally. If not, one or more could become overheated and become expulsion and not be welded.
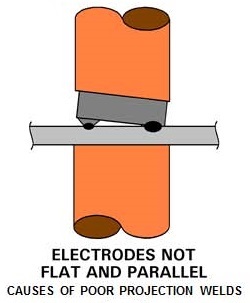
ALIGNMENT ISSUES
PROJECTION SHAPE, SIZE & CONSISTENCY
If the projection shape, size or count is not consistent, there will be a very big problem. A standardized schedule would be impossible. Every time the part varies the results would vary. Projection diameter and height must be consistent or there will be considerable variation in weld results.
The projection design does most of the heavy lifting that an electrode would do in spot welding. In projection welding electrodes merely apply the force and current into the part. They do not directly conduct the heat. They must be aligned properly and conform to the part to maintain alignment (frequently flat surfaces suffice) and position as described above. Material selection is generally chosen for mechanical wear considerations. Copper Alloys RWMA Class 2 or 3 are the first choice. For heavier duty nut welding refractory faced electrodes RWMA Class 11 are frequently used with and without locator pins.
THESE ITEMS ARE ADDRESSED FULLY IN ANOTHER ARTICLE IN THIS WEBSITE:
How do you develop a projection welding process?
This article explains the importance of fast force follow up, good alignment, properly shaped projections and electrode selection. It also addressed initial process development. This article has the explanation of the Do’s and Don’ts for projection welding.
Reference: AWS C1.1 Recommended Practices for Resistance Welding
AWS J1.3 Specification for Materials Used In Resistance Welding Electrodes and Tooling
AWS J1.2 Guide to Installation and Maintenance of Resistance Welding Machines

