The answer to this depends upon the material being seam welded. Highly conductive softer materials (Aluminum) will be seam welded with Class 1. Stronger more resistive material (low carbon steels) would use Class 2. High strength resistive material (nickel base and stainless steel) would use Class 3. This is the same as for spot welding electrode selection and can be found in various industry charts in AWS and other publication.
The person making this inquiry was not sure what wheel material he had in this stainless cloth to stainless sheet application. He was experiencing excessive pickup on the wheel face. This could be due to the unknown alloy wheel or it could be normal. Wheels just like spot welding electrodes will experience pick up and mushrooming during normal use.
In many seam welding applications a knurling wheel is installed on the wheel periphery which continually trims the edges and roughens/knurls the face. This makes sure that the weld wheel is always in the same condition without build up. This is a continuous dressing operation. Sometimes the knurler functions as the wheel drive mechanism. In other designs it rides on the wheel and merely dresses.
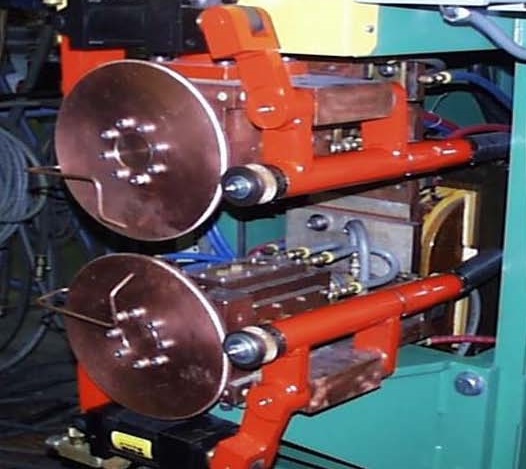
KNURL DRIVE/DRESSER
Another issue to address is cooling. The wheel hub should always be cooled. In this case flood cooling the weld joint might be in order to reduce the electrode pickup.
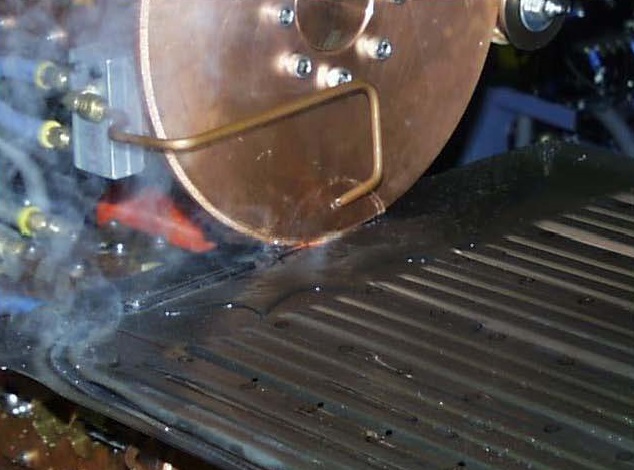

FLOOD COOLING AT THE SEAM WELDING
Proper force is also important. If the force is less than desired, it will increase contact resistance between the wheel face and the part. The wheel face will run hotter and more pickup will occur. Proper increased force will reduce this wheel contact resistance and move the heat to the desired weld interface.
A proper weld schedule and cooling is designed to weld the part and keep the face of the wheel as cool as possible as long as possible.
OTHER RELATED ARTICLES ON THIS SUBJECT:
WHAT MATERIALS ARE USED FOR SEAM WELDING WHEELS?
DO SEAM WELD WHEELS NEED TO BE DRESSED?
WHAT IS THE PROPER AMOUNT OF WATER COOLING FOR SEAM WELDING?
WILL COATED 0.80 MM MATERIAL BE MORE PRONE TO PRODUCE SEAM WELD BURRS THAN BARE MATERIAL?
References: AWS C1.1 Recommended Practices for Resistance Welding
RWMA Resistance Welding Manual 4th Edition
CMW Inc. Catalog

