There are two types of drives for seam weld wheels. One is driven by the central hub, direct drive. The other is driven by knurled wheels riding on the perimeter of the seam welding wheels, indirect drive. There are pros and cons for both systems.
KNURL DRIVE
The knurl drive, indirect drive system provides a constant linear wheel speed at all wheel diameters. This allows the use of two wheels of different size. Frequently it is advantageous to use a smaller seam welding wheel on one side. The knurl driven system accommodates this easily. The knurl is also used to continuously dress the wheels on every rotation so that fresh wheel material is always being used to make the weld. The knurl imprints a knurl pattern on the wheel which enables the wheel to grip the workpiece and move it without slipping. One negative is it may leave a knurl patter on the part face. Water is frequently sprayed on the knurl drive area to remove loose material and keep the heat down. A knurl driven machine may cost up to 20% more than a direct drive machine.
DIRECT DRIVE
The alternative is a central axis shaft driven machine (direct drive). Either one or both wheels may be driven. If both wheels are driven, they must be the same diameter in order to travel at the same lineal speed. If only one wheel is driven, the size can vary. As the wheels are dressed or wear the lineal speed will change and must be compensated for to maintain weld spacing. To dress the wheels they are frequently removed and dressed off line on a lathe. The option is to design an automated dresser. At the proper time the automated dressing tool would move into position and dress each or both wheels as desired. Every time you dress the wheels, their diameter is changing and therefor the rotational speed of direct driven wheels must be adjusted to maintain the desired lineal speed and weld spacing.

Seam Welder with Knurl Drive
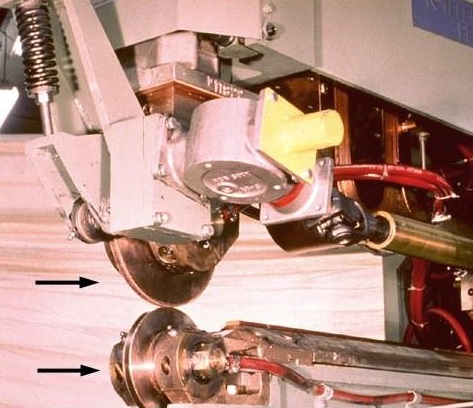
Upper Direct Drive Barrel Seam Welder
Part specifications size and geometry will probably dictate which drive system is best for the application.
Reference: RWMA – Resistance Welding Manual Section 4

